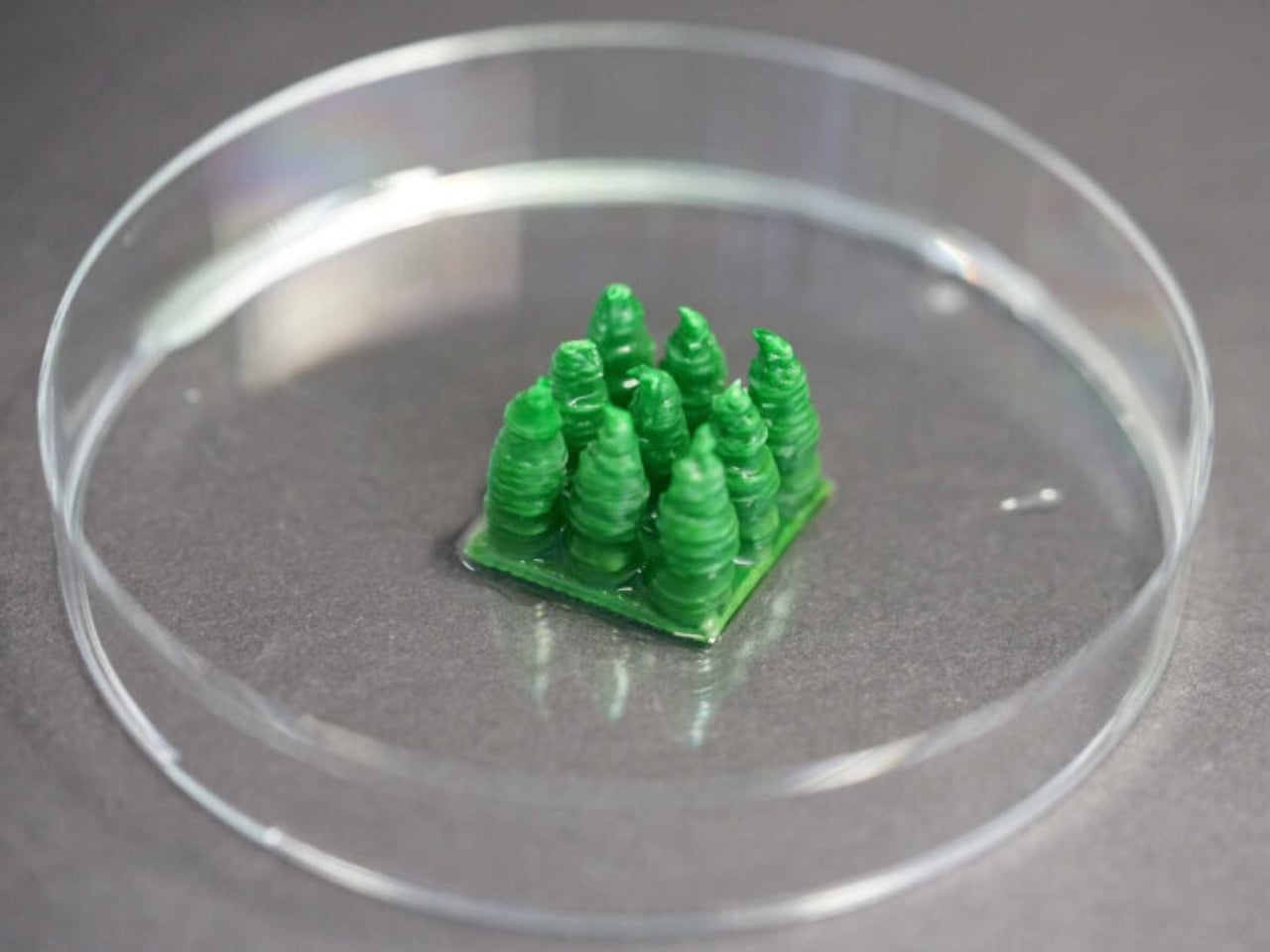

Buildings are responsible for a huge share of global carbon emissions, especially during the production of materials like cement. Traditional concrete manufacturing is one of the biggest sources of CO2 worldwide. If we can switch to materials that don’t just stop this but even use CO2 to our advantage, then we can make a big difference in fighting climate change. Imagine a future where our homes and offices not only look beautiful but also help clean the air by capturing carbon dioxide (CO2).
Thanks to a team of scientists at ETH Zurich, that future might be closer than we think. They have developed a remarkable new building material that doesn’t just sit there. It’s actually alive and actively helping the planet. This groundbreaking material is a type of concrete, but with a twist: it contains living bacteria. These aren’t just any bacteria as they are specially chosen because they can turn carbon dioxide from the air into solid minerals. That means while regular concrete actually releases CO2 during its production, this living material absorbs it, helping to reduce greenhouse gases in our atmosphere.
Designer: ETH Zurich
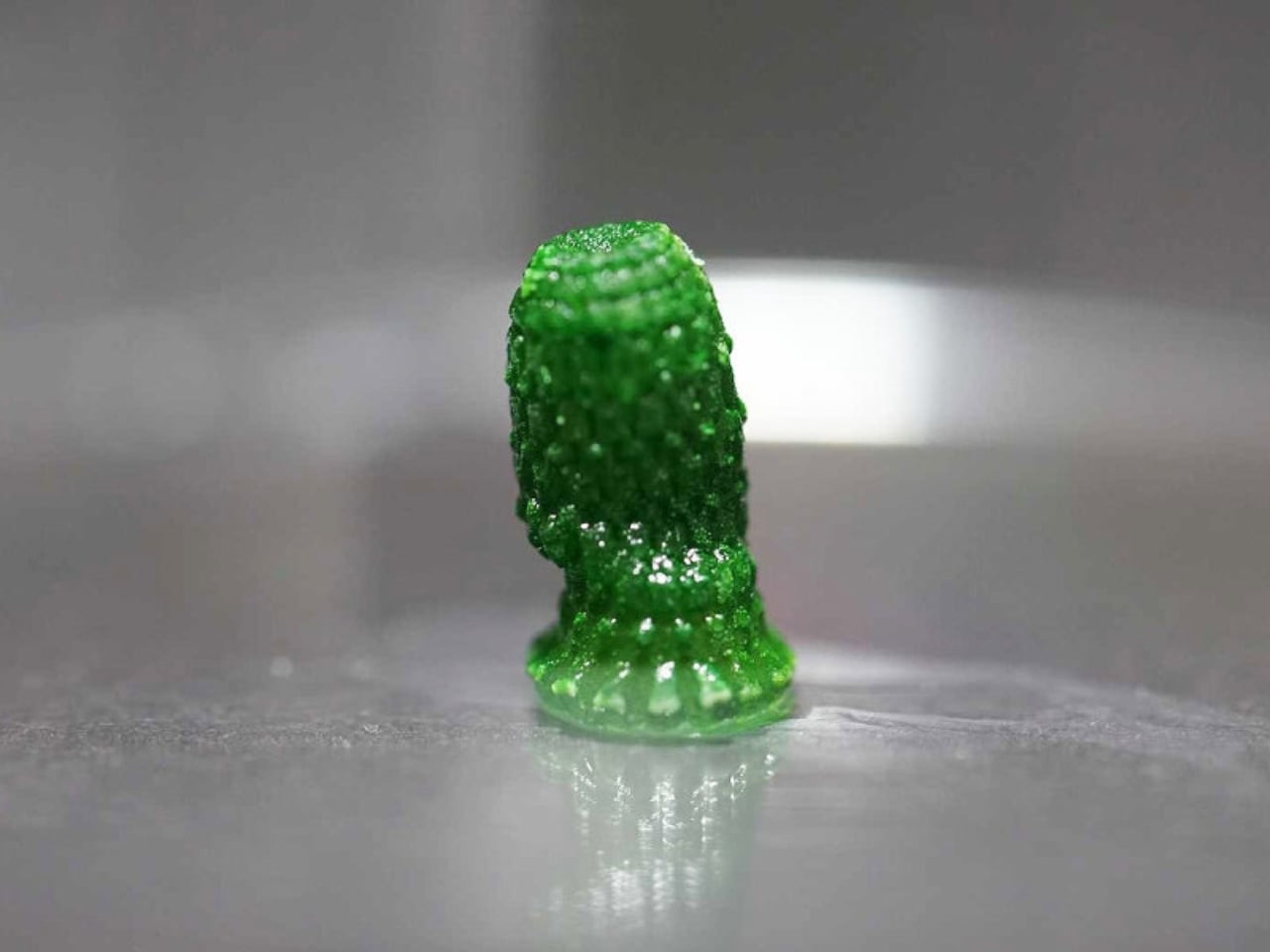

Inside the material, millions of bacteria are hard at work. These bacteria are fed a mixture of nutrients, including calcium. When they “eat,” they react with CO2 in the air, producing solid calcium carbonate. This process is similar to how seashells form in nature. Over time, the bacteria help the material grow stronger while trapping more carbon dioxide. The scientists designed their material to be porous, which means it has lots of tiny holes. These holes give bacteria plenty of room to live and work, while also allowing air to pass through so the bacteria can capture CO2 efficiently.
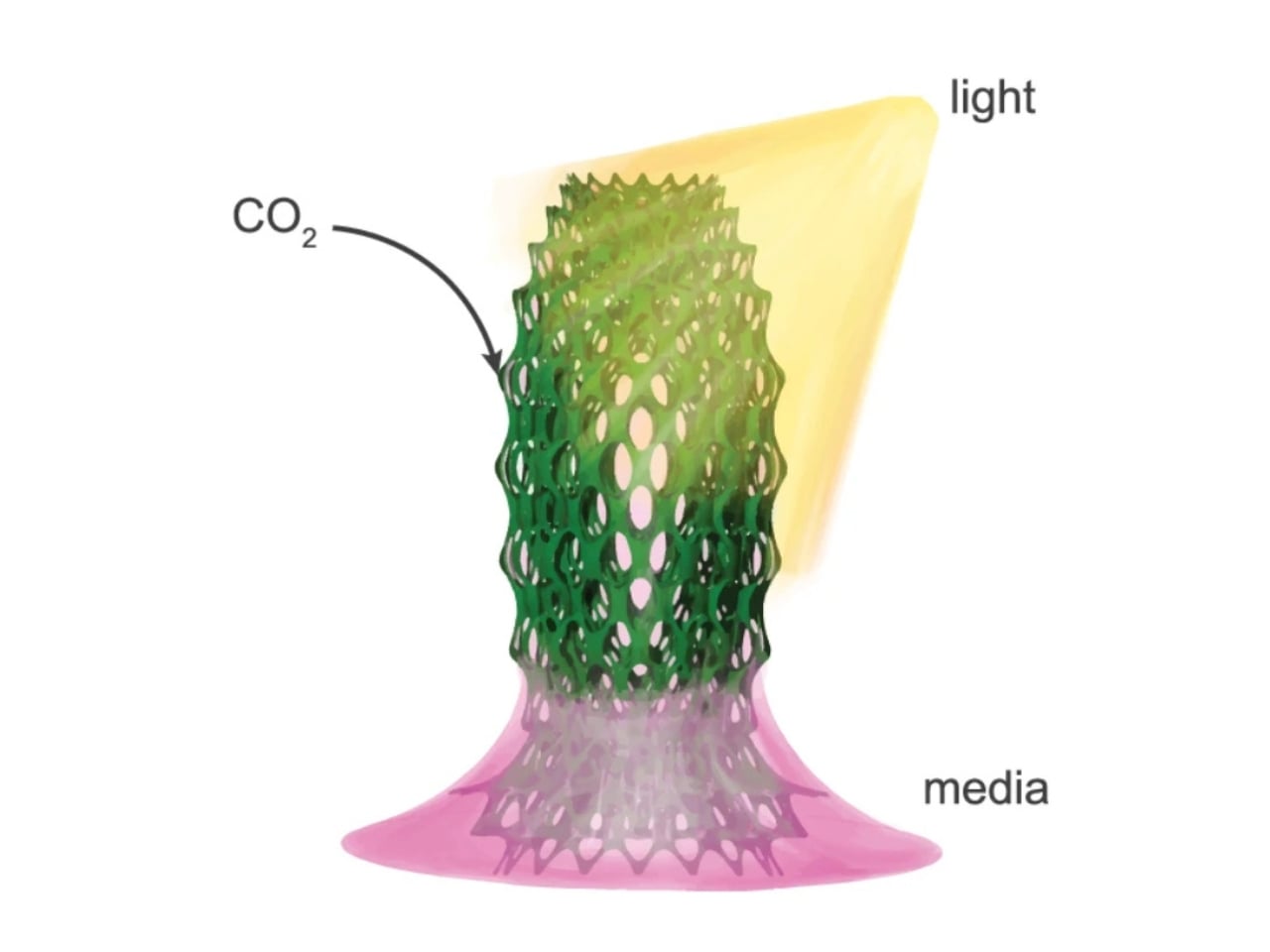
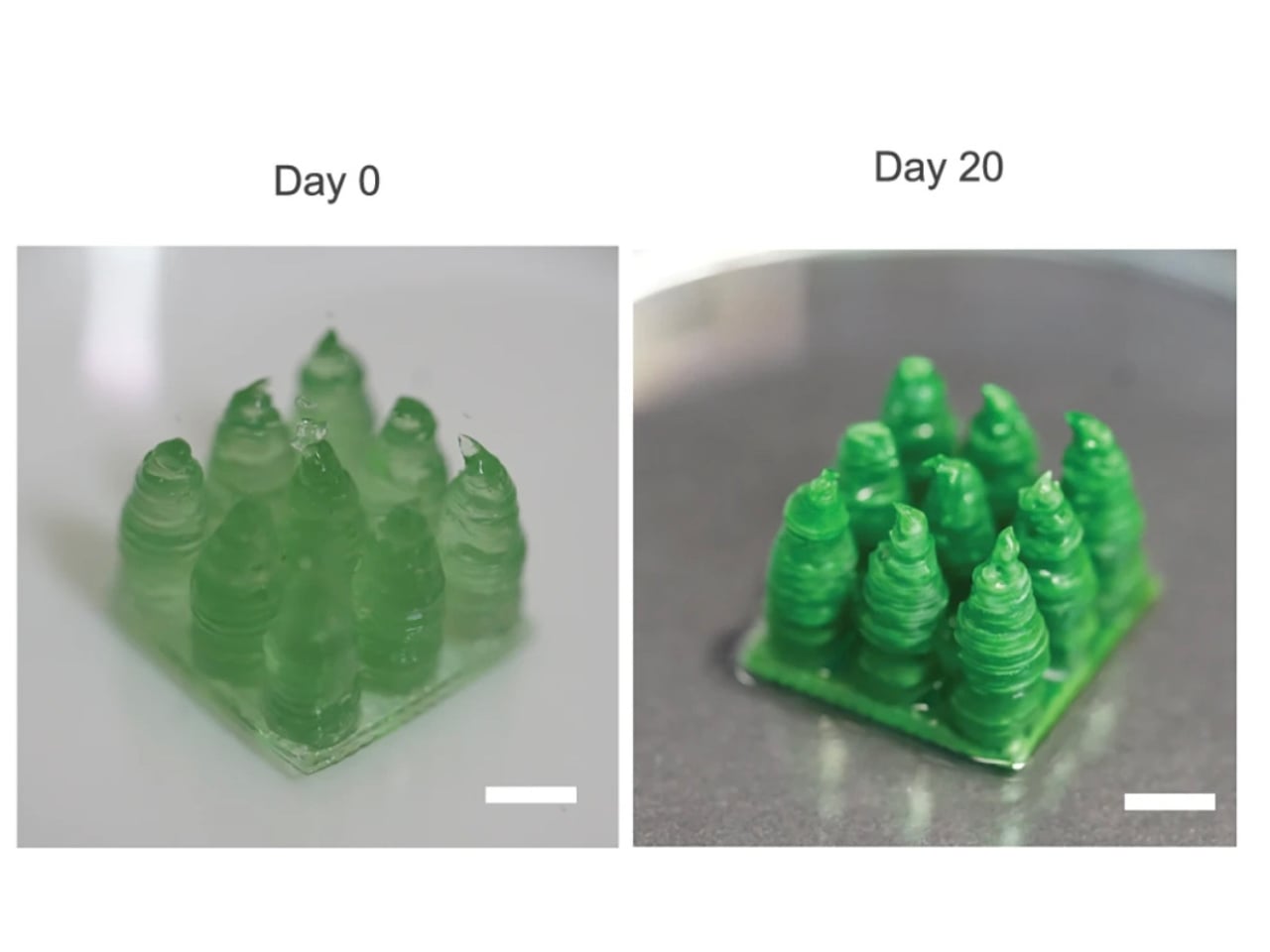
The new living material could be used in walls, floors, or even outdoor structures. Imagine a city full of buildings that quietly soak up CO2 day after day, making the air cleaner for everyone. But the benefits don’t stop there. The production of this living material uses less energy than regular concrete. Plus, the process is designed to be sustainable from start to finish. The bacteria don’t need fancy care—they just need a bit of food and the right conditions to thrive. If a piece of the material breaks, it can even “heal” itself. The bacteria inside can repair small cracks by producing more calcium carbonate, just like how your skin heals a cut. This could help buildings last longer and require less maintenance.
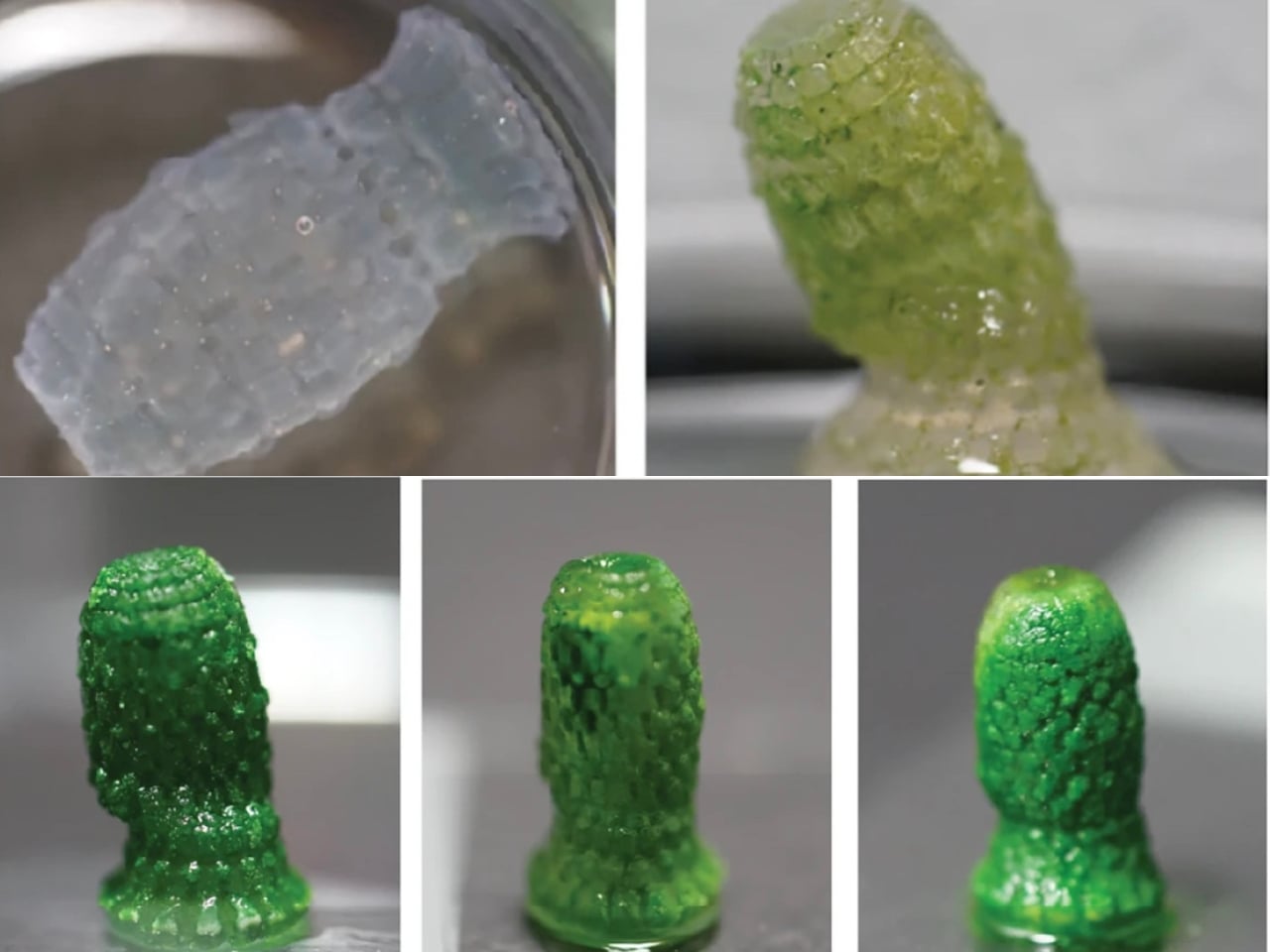

The research team is still working on perfecting their creation. They want to make sure the material is strong enough for real-world use and figure out the best ways to produce it on a large scale. There are also questions about how the bacteria will behave over many years and in different climates. Still, the early results are very promising. This living building material could offer a win-win solution: helping to build the cities of tomorrow while also cleaning up the air today.
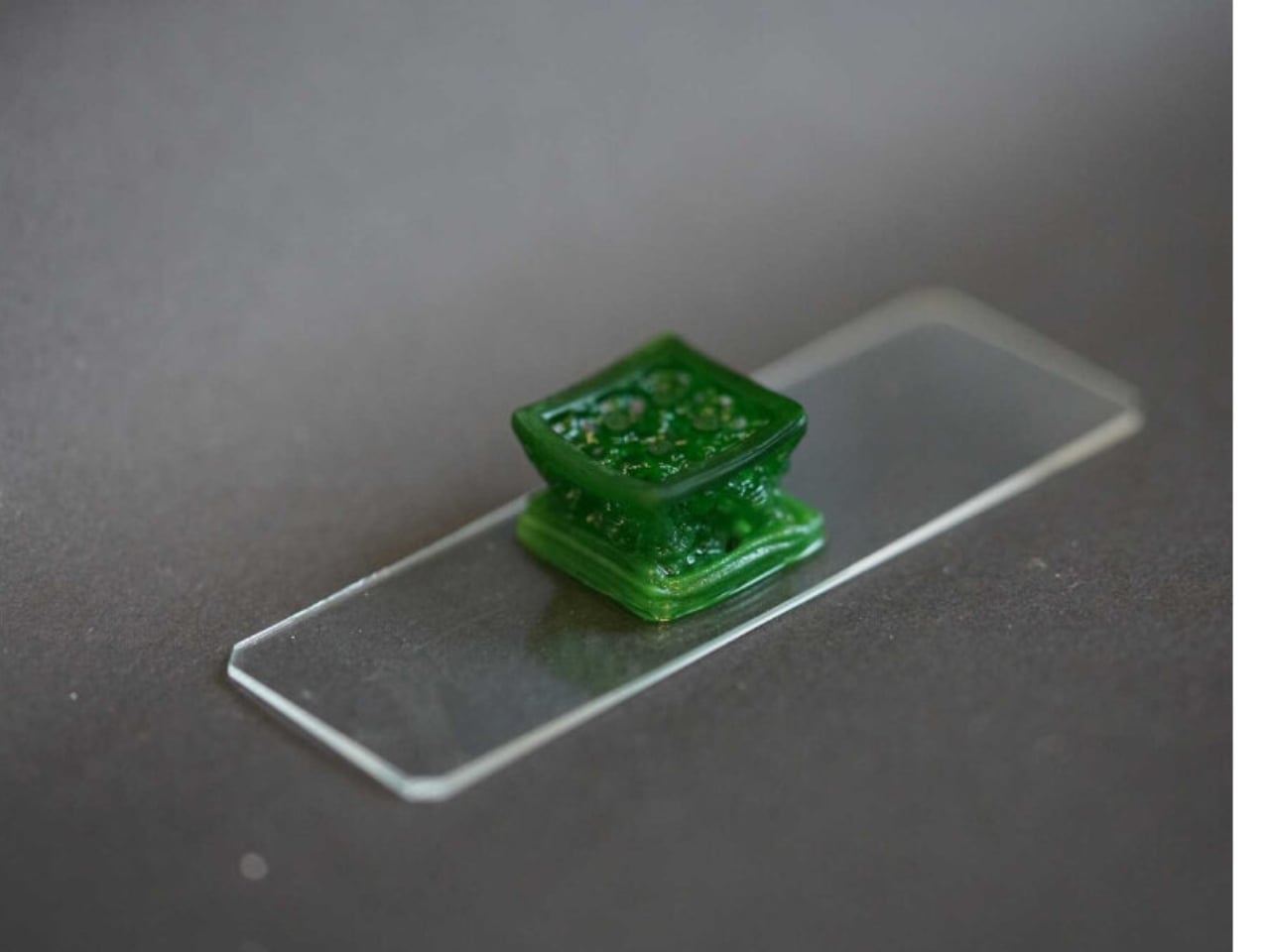
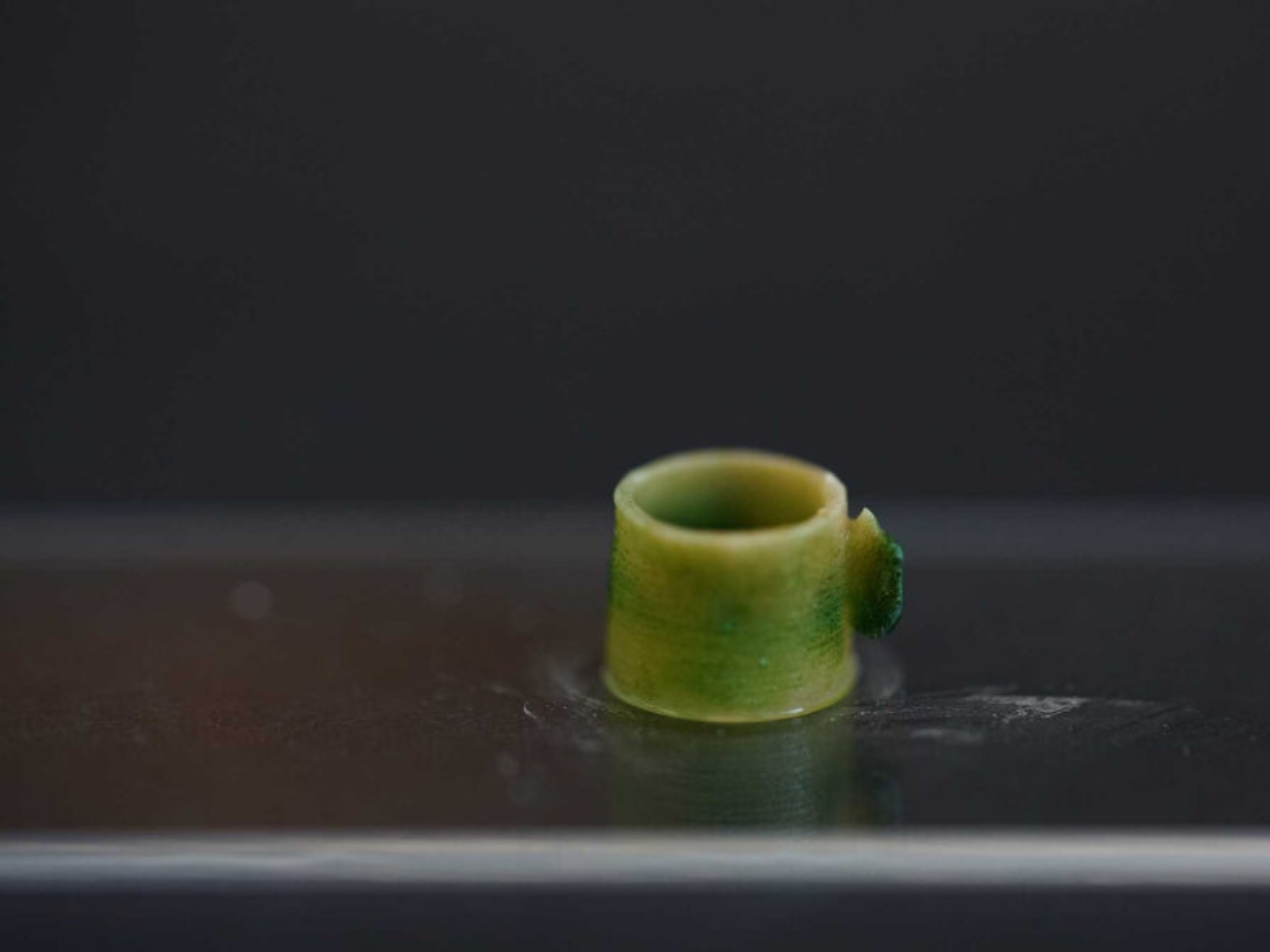


The post Scientists create living building material that traps carbon dioxide first appeared on Yanko Design.







