In 1989, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) partnered with the Associated Landscape Contractors of America (ALCA) to conduct a Clean Air Study. Led by Dr. B. C. Wolverton, the study provided a comprehensive list of plants that are highly effective at purifying indoor air. The research demonstrated that plants have the ability to filter pollutants such as benzene, ammonia, and formaldehyde, which helps mitigate the effects of Sick Building Syndrome. Certain tropical houseplants were found to be particularly efficient in removing formaldehyde, trichloroethane, benzene, and other harmful substances from the air, replacing them with oxygen. According to the report, it is recommended to have at least one plant for every hundred square feet of indoor space, be it at home or in the office.
Designer: Ugly Duckling ID


Common Indoor Pollutants
Trichloroethylene, formaldehyde, benzene, xylene, ammonia, nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and suspended particulate matter (SPM) are harmful substances found in various products and environments.
• Trichloroethylene, present in inks and pa2ints, can lead to symptoms such as dizziness and coma.
• Benzene, used in plastics and tobacco smoke, may result in drowsiness and unconsciousness.
• Formaldehyde, commonly found in paper products and fabrics, can cause irritation and swelling in the respiratory system.
• Ammonia, found in cleaning products, can cause eye irritation and sore throat.
• Xylene, present in rubber and vehicle exhaust, can lead to liver and kidney damage.
• NO2 and SO2, emitted by vehicles and factories, can harm the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
• SPM, small particles in the air, can irritate the eyes and respiratory tract and contribute to long-term health issues like asthma and cardiovascular problems.
Top 12 Air-Purifying Plants
1. Areca Palm (Dypsis lutescens)
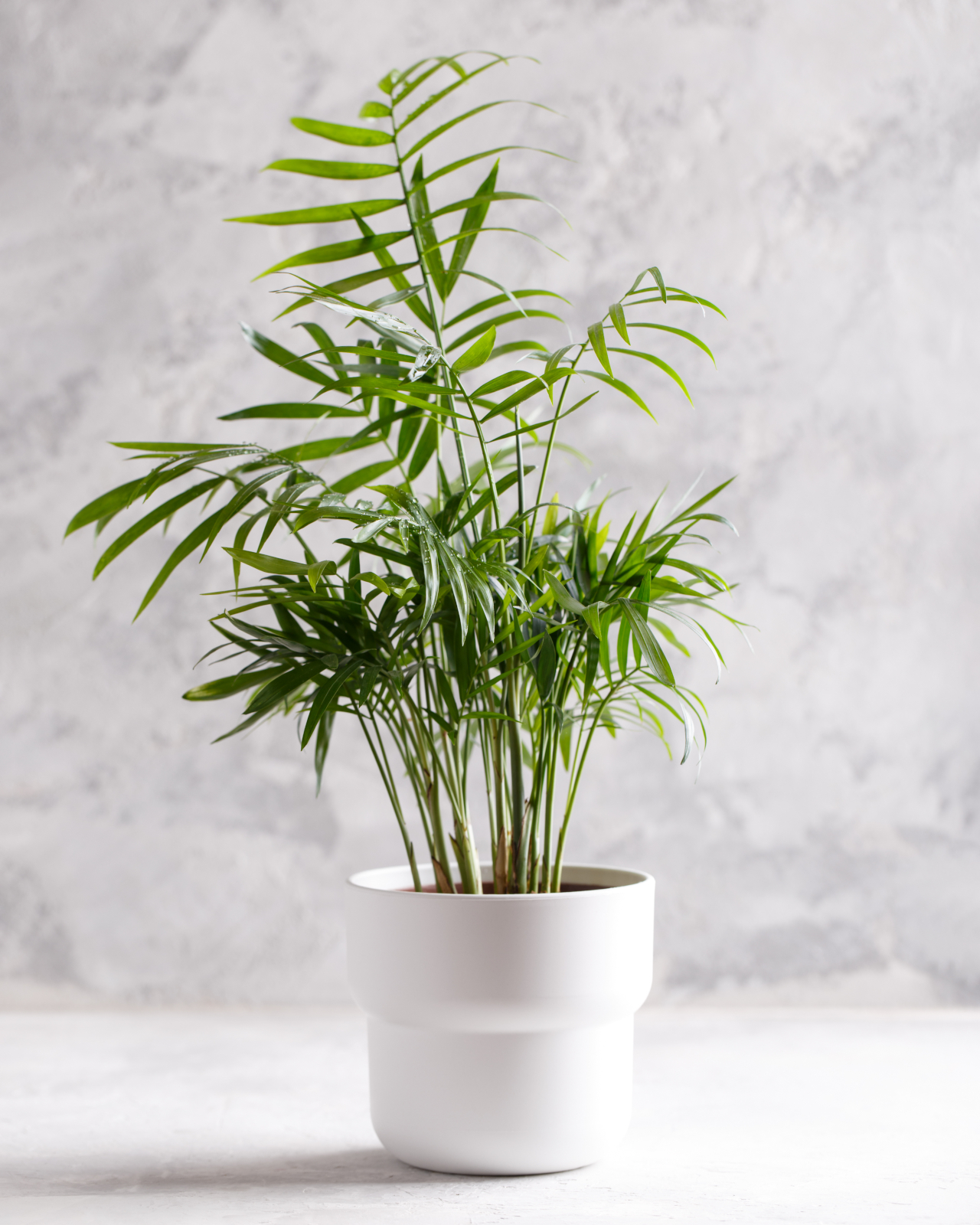

Image courtesy of: Spaces
The Areca palm, native to Madagascar, is a popular foliage houseplant known for its ability to purify the air by removing formaldehyde, xylene, and toluene. As a houseplant, it thrives indoors and can tolerate both shade and bright light. It requires less frequent watering and prefers temperatures ranging from 15 to 35 degrees Celsius and it adds beauty and charm to any indoor space.
2. Snake Plant (Sansevieria trifasciata)
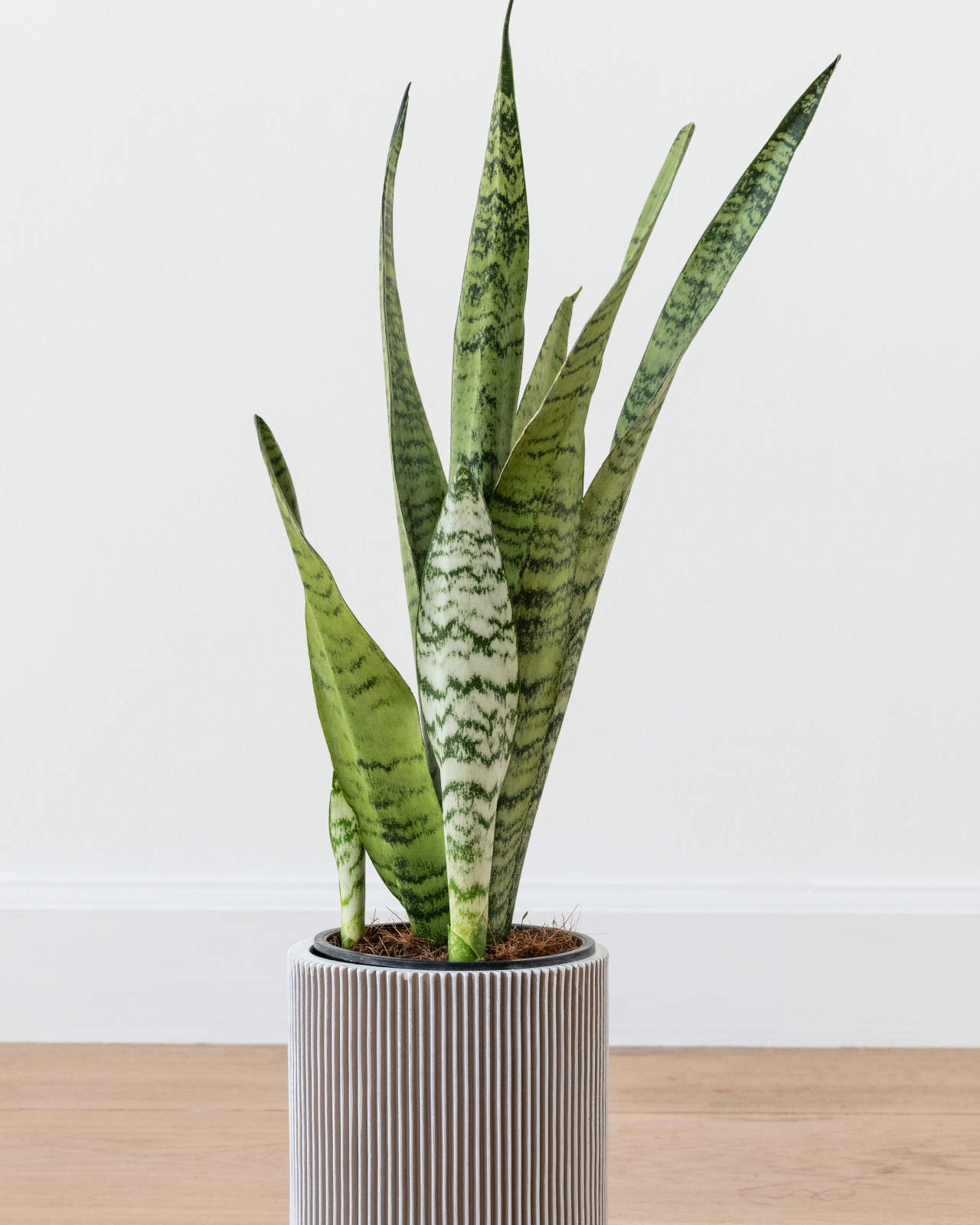

Image courtesy of: Rawpixel
Sansevieria, commonly known as Mother-in-law’s tongue or Snake plant, is an incredibly resilient indoor plant that thrives even in low light conditions. It is a perfect choice for those seeking a low-maintenance plant as it requires infrequent watering. Moreover, Sansevieria has been recognized as one of the most effective air-purifying plants, capable of eliminating benzene, formaldehyde, trichloroethylene, xylene, and toluene from the surrounding air. It can adapt to various temperature ranges, from 5 to 45 degrees Celsius, making it suitable for different climates.
3. Money Plant (Epipremnum aureum)
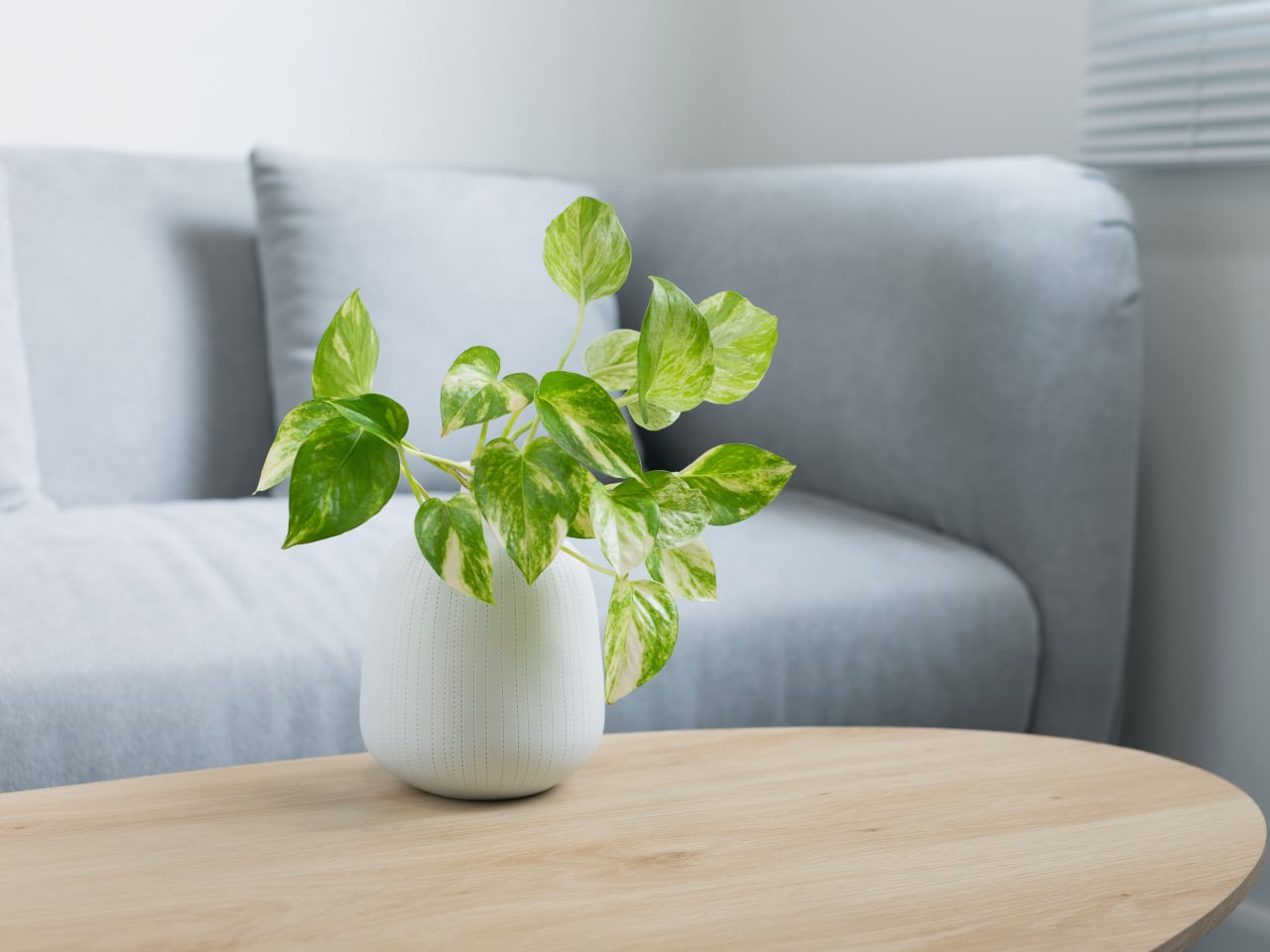

Image courtesy of: eddows_arunothai
The money plant, belonging to the Araceae plant family, is a popular houseplant found in French Polynesia. It is highly adaptable and can thrive in various indoor environments. It has the ability to effectively purify the air by removing benzene, formaldehyde, trichloroethylene, xylene, and toluene. As a houseplant, its growing habits and characteristics are as follows: it prefers indoor locations, tolerates shade and artificial light, requires less frequent watering, and can withstand temperatures ranging from 15 to 45 degrees Celsius.
4. English ivy (Hedera helix)
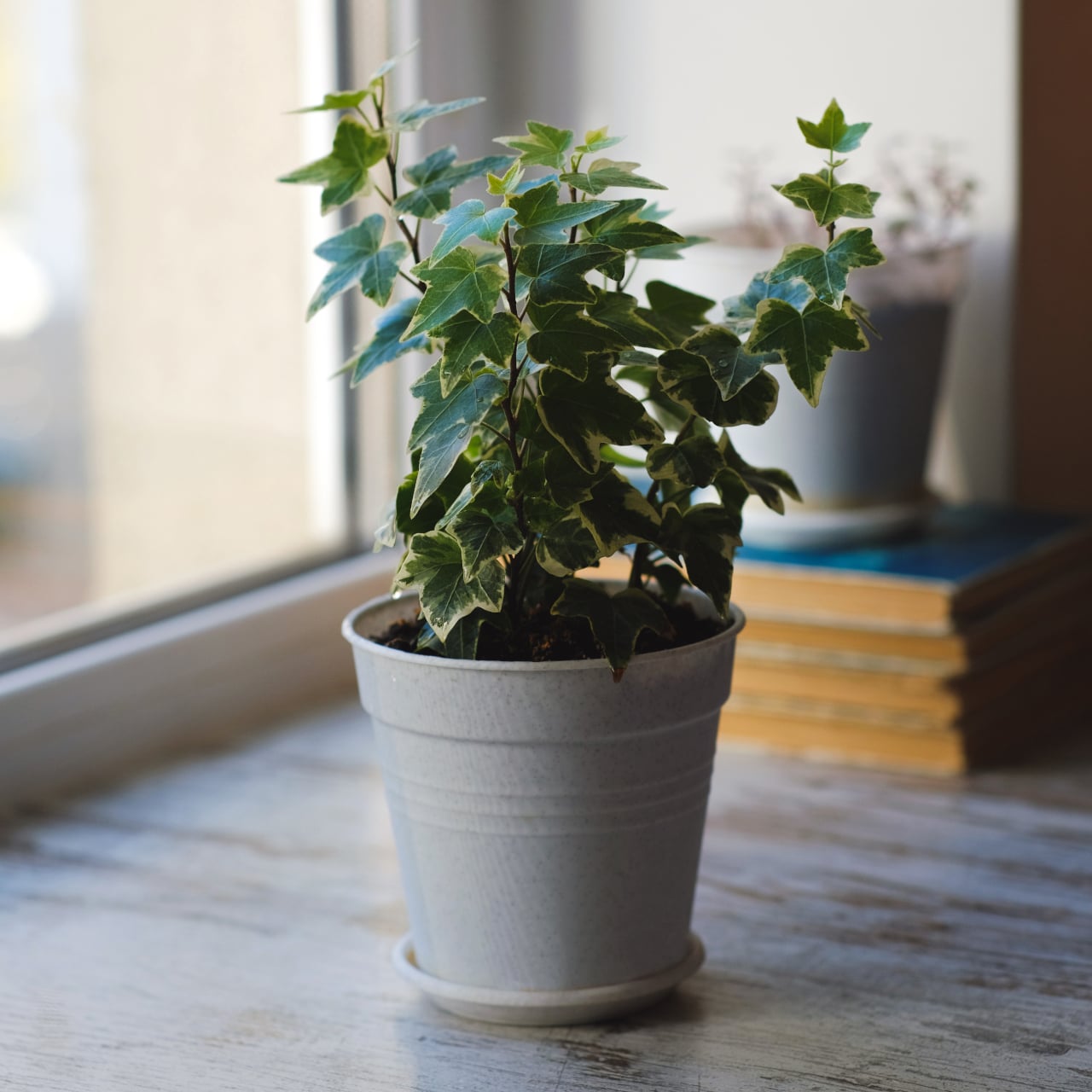

Image courtesy of: kolomietsolena
English Ivy, a flowering plant from the Araliaceous family, is a highly popular vine plant in Europe. It is native to most of Europe and Western Asia. Notably, English Ivy has been identified as one of the most efficient plants in removing benzene, formaldehyde, trichloroethylene, xylene, and toluene from the air. As a houseplant, its growing habits and characteristics include indoor location preference, tolerance to shade and artificial light, less frequent watering requirements, and a temperature range of 5 to 30 degrees Celsius.
5. Peace Lily (Spathiphyllum)
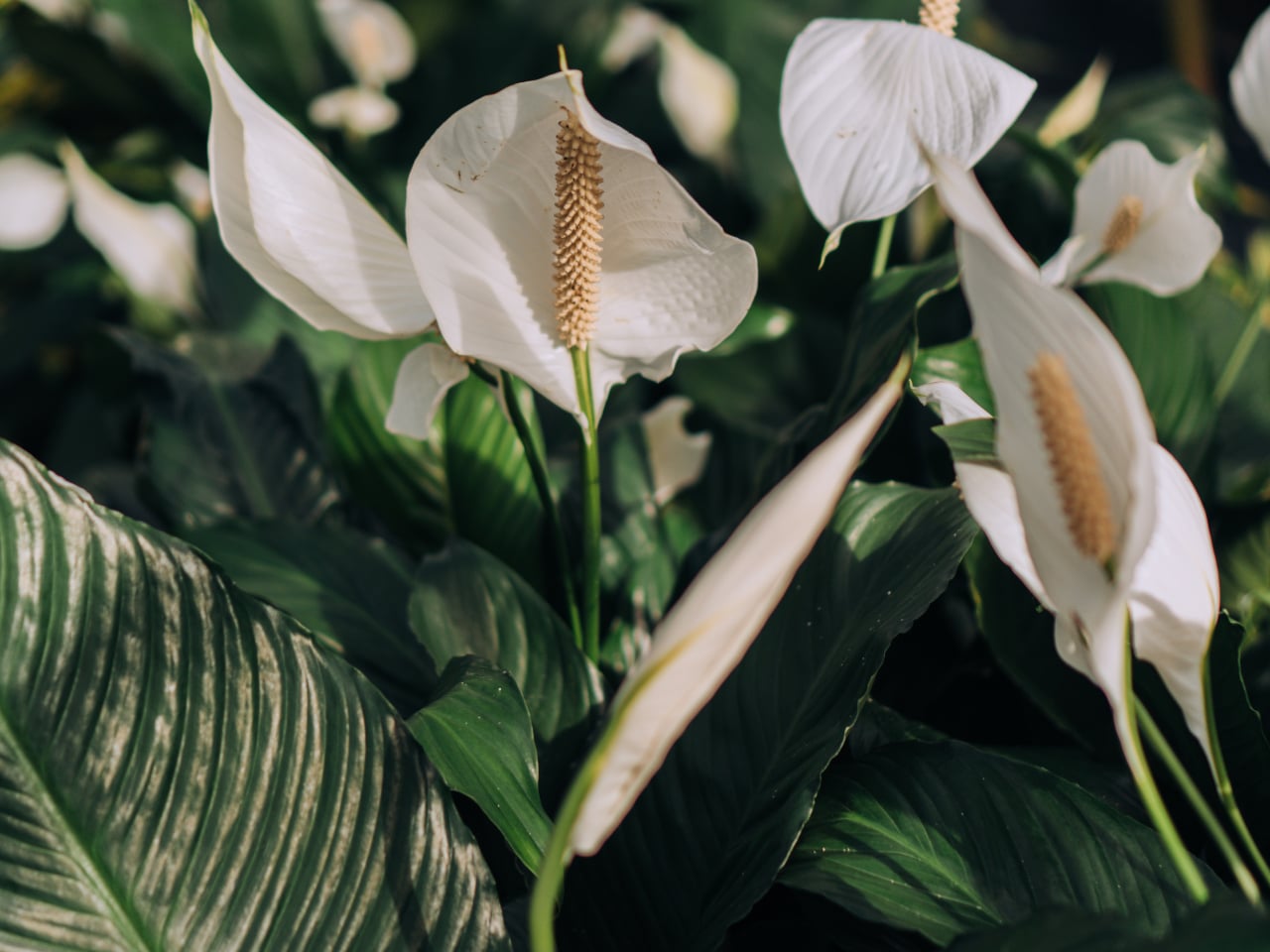

Image courtesy of: Elisall
The peace lily, belonging to the Araceae plant family, is a well-known indoor plant. It has been identified as one of the most efficient plants in eliminating benzene, formaldehyde, trichloroethylene, ammonia, xylene, toluene, and other pollutants from the air. As a houseplant, it thrives indoors and can tolerate both shade and artificial light. It requires less frequent watering and prefers temperatures ranging from 16 to 32 degrees Celsius.
6. Barberton Daisy (Gerbera jamesonii)
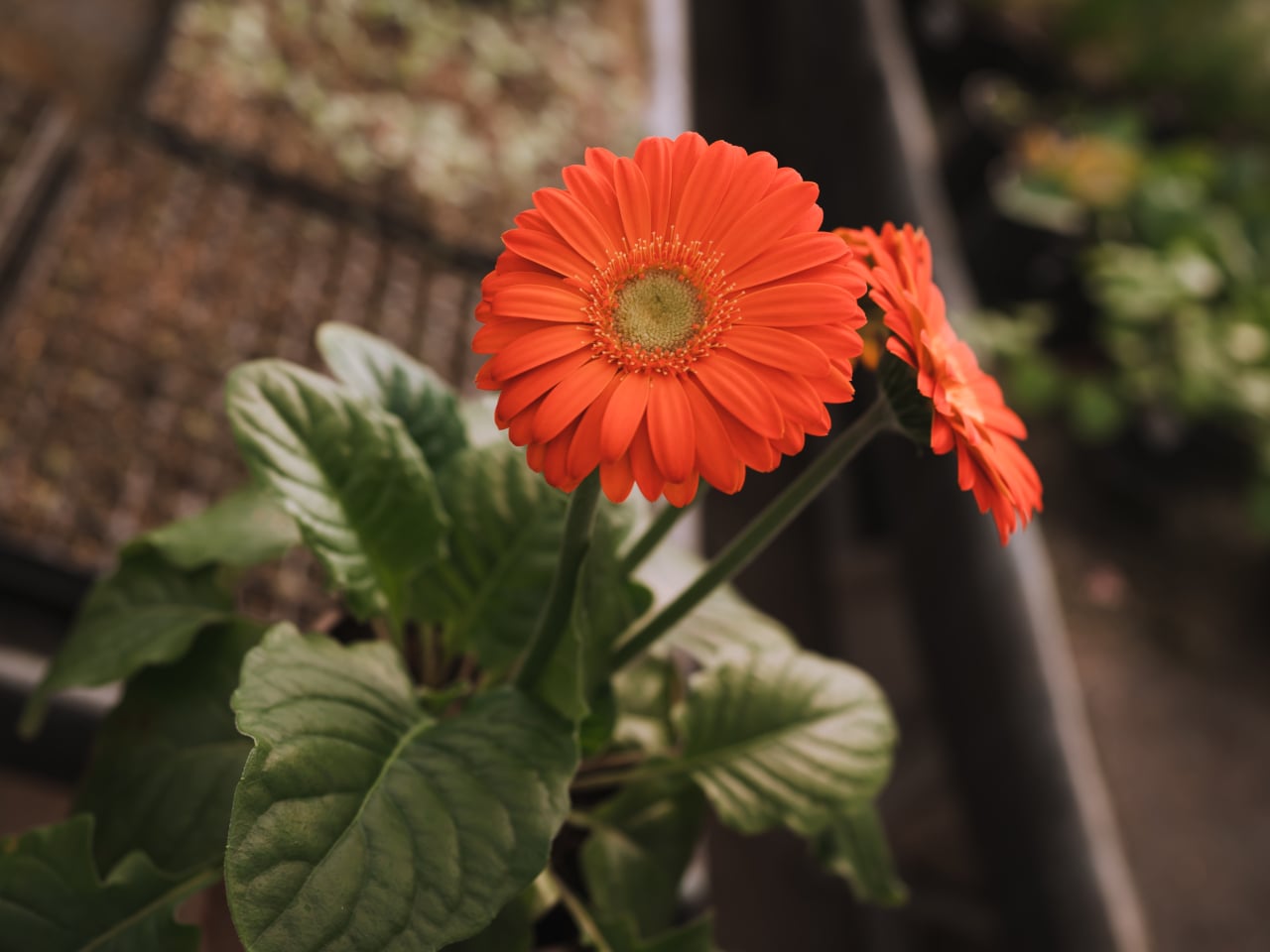

Image courtesy of: natanavo
Gerbera, a genus of flowering plants in the Asteraceae family, is renowned for its vibrant and lustrous flowers. It is a popular choice due to its ability to withstand adverse weather conditions and thrive in bright light. Notably, Gerbera is effective in purifying the air by eliminating benzene, formaldehyde, and trichloroethylene. As a houseplant, it flourishes indoors, tolerating both shade and bright light. It requires less frequent watering and prefers temperatures ranging from 15 to 25 degrees Celsius.
7. Chinese Evergreens (Aglaonema Modestum)
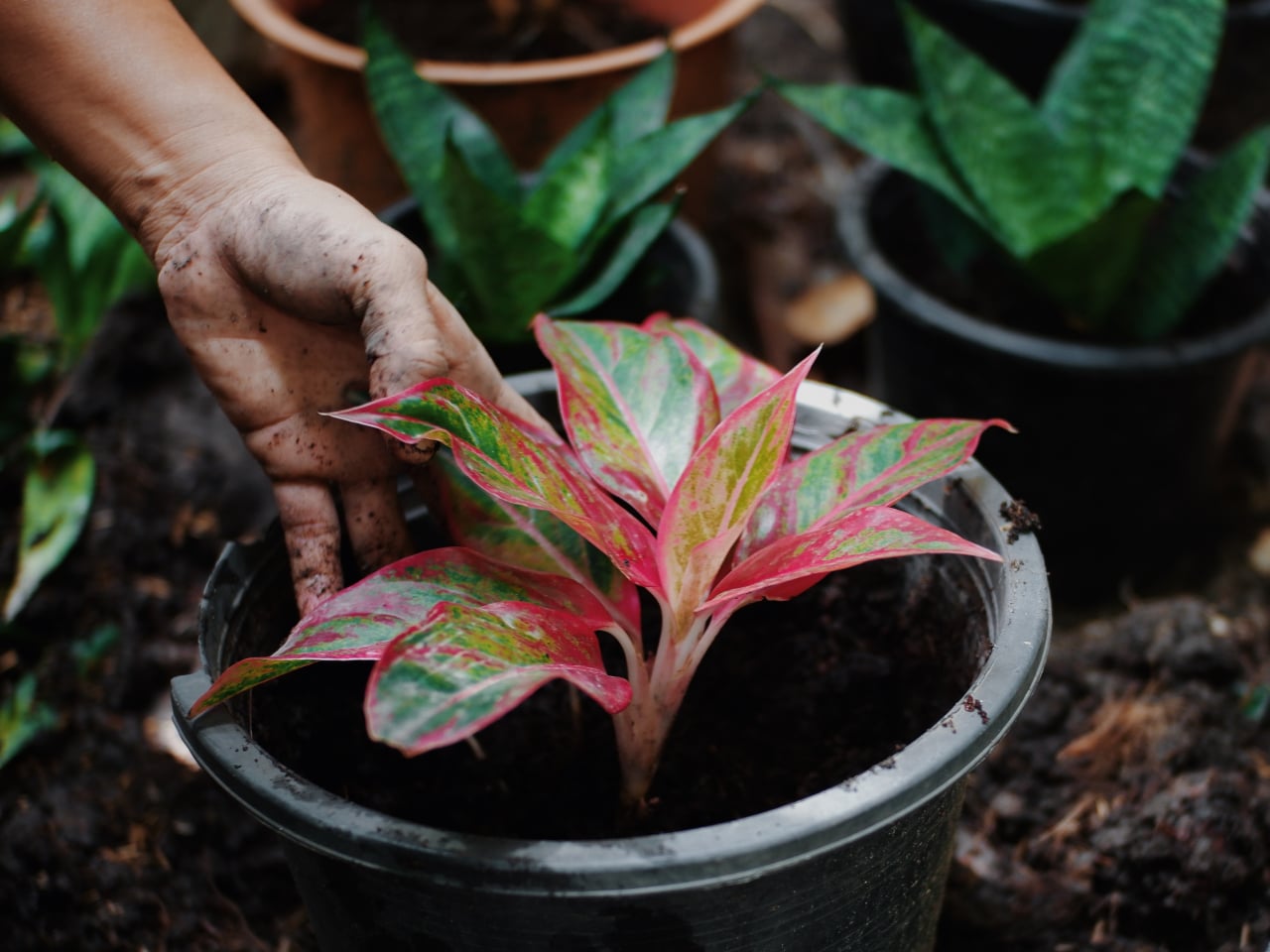

Image courtesy of: Jsttanrak
Aglaonema, a member of the Araceae family, is a popular indoor plant originating from tropical and subtropical regions of South Asia. With over 100 popular varieties, it is both visually appealing and low-maintenance. Notably, Aglaonema is known for its ability to cleanse the air by removing benzene and formaldehyde. As a houseplant, it thrives in indoor locations, tolerates shade and artificial light, requires less frequent watering, and prefers temperatures ranging from 15 to 30 degrees Celsius.
8. Spider Plant (Chlorophytum comosum)
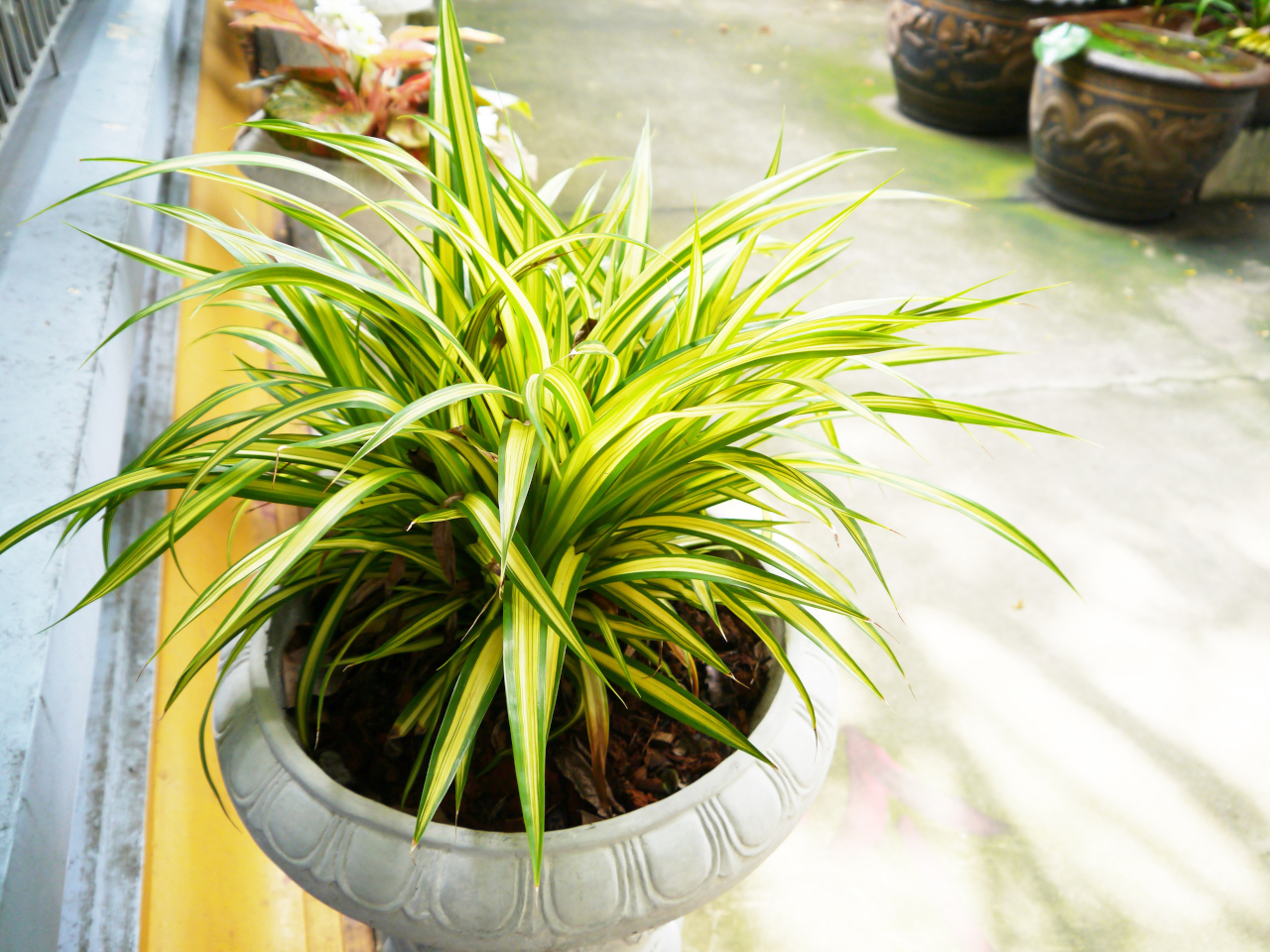

Image courtesy of: araleboy
Chlorophytum comosum, a member of the Asparagaceae plant family, originates from southern Africa. This popular houseplant, known as the spider plant, is not only elegant and fast-growing but also easy to care for. A report by the university’s Cooperative Extension Service highlighted the spider plant as one of the top varieties for effectively removing VOCs. It has been found to cleanse the air by eliminating formaldehyde, xylene, and toluene. As a houseplant, the spider plant thrives indoors, tolerating shade and artificial light, requiring less frequent watering, and favoring temperatures ranging from 15 to 30 degrees Celsius.
9. Aloe Vera (Aloe barbadensis mill)
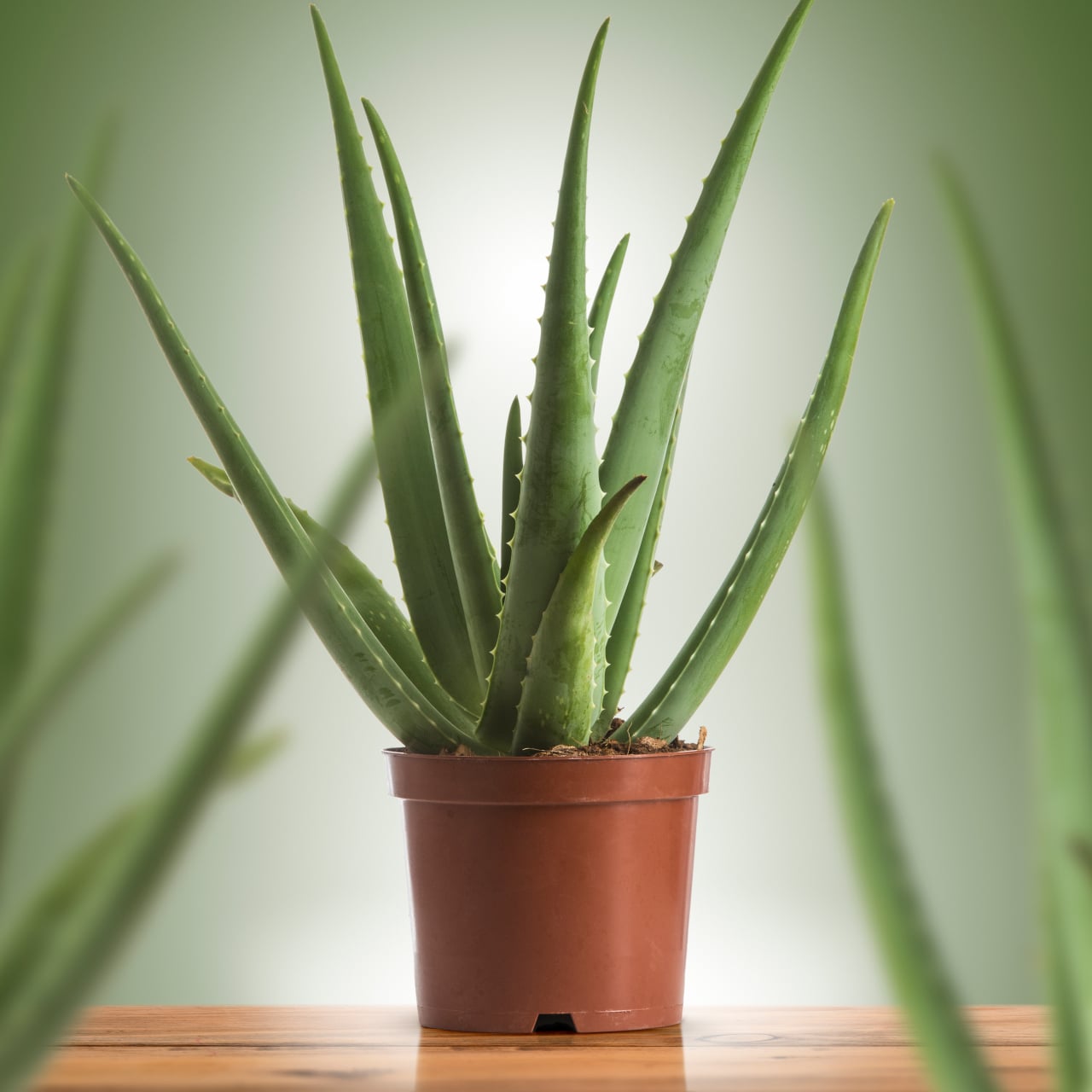

Image courtesy of: Olivier_Le_Moal
Aloe vera, a succulent plant belonging to the Asphodelaceae family, is a remarkable plant known for its numerous benefits and medicinal uses since ancient times. It can withstand adverse weather conditions and thrives in bright light, making it suitable for deserts. Aloe vera is also effective in purifying the air by eliminating benzene and formaldehyde. As a houseplant, it prefers indoor locations, tolerates both shade and bright light, requires less frequent watering, and can thrive in temperatures ranging from 15 to 45 degrees Celsius.
10. Rubber plant (Ficus elastica)
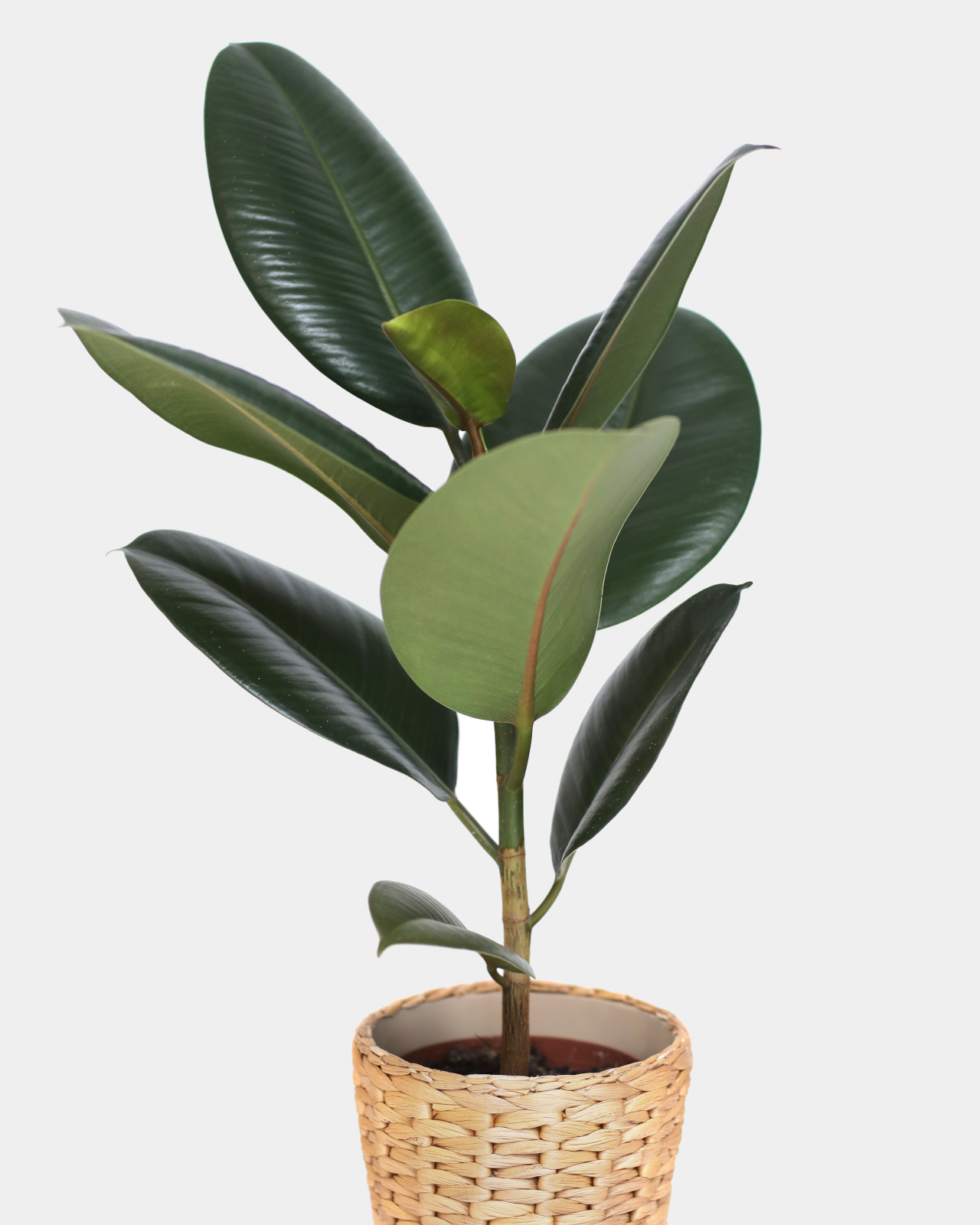

Image courtesy of: andriymedvediuk
The Rubber Plant, classified under the genus Ficus in the Moraceae plant family, is native to South Asia. This houseplant has been discovered to effectively eliminate formaldehyde from the air. As a houseplant, it thrives indoors, tolerating both shade and artificial light. It requires less frequent watering and prefers temperatures ranging from 15 to 30 degrees Celsius.
11. Boston Fern (Nephrolepis exaltata)
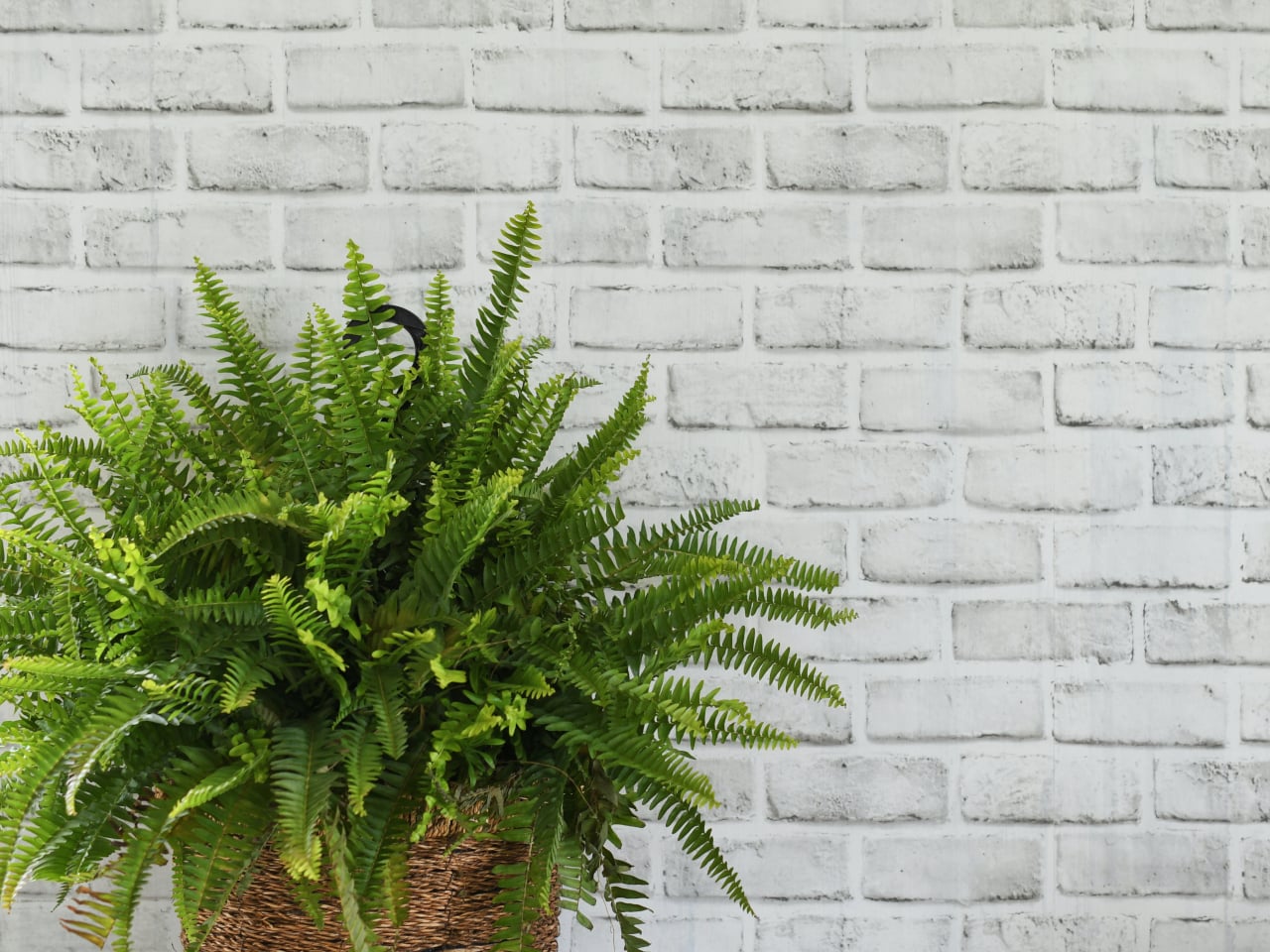

Image courtesy of: MargJohnsonVA
The Boston fern, belonging to the Nephrolepidaceae family and the Nephrolepis genus, is native to humid forests and swamps. It is known for its ability to effectively eliminate formaldehyde, xylene, toluene, airborne germs, molds, and bacteria from indoor air. As a houseplant, it thrives in indoor locations, tolerating both shade and artificial light. It requires frequent watering and prefers temperatures ranging from 15 to 35 degrees Celsius.
12. Bamboo Palm (Chamaedorea seifrizi)

Image courtesy of: Natabuena
The Bamboo palm, part of the Chamaedorea genus in the Aceraceae plant family, is one of the 107 species within its genus. This plant thrives in shady and humid conditions, often found growing under trees in rainforests. It is known for its ability to effectively remove benzene, formaldehyde, trichloroethylene, xylene, and toluene from the air. As a houseplant, it prefers indoor locations and can tolerate shade and artificial light. It requires frequent watering and thrives in temperatures ranging from 10 to 35 degrees Celsius.
The post Breathing Fresh: NASA’s Top 12 Air-Purifying Plants for Cleaner Indoor Spaces first appeared on Yanko Design.