The appeal of tiny homes continues to rise as more people are drawn to the simplicity, affordability, and sustainability they offer. However, creating a cozy, functional, and lasting tiny home necessitates taking your local climate and environment into account. In this editorial, we’ll explore how to tailor your tiny home to thrive in various climates, offering practical design considerations for temperate, tropical, arid (desert), cold, and coastal environments. From personal anecdotes to professional insights, this article will guide you through what to prioritize to ensure your tiny home is both comfortable and efficient.
The environment where you plan to build isn’t just a backdrop; it’s a critical element that influences construction materials, design aesthetics, and long-term livability. A well-designed tiny home reflects thoughtful consideration of the climate, turning potential challenges into advantages. Whether you’re dealing with extreme temperatures, high humidity, frequent storms, or snowfall, your tiny home can be an oasis of comfort and functionality if built with the right principles in mind. Let’s dive into how to design your tiny sanctuary to harmonize with the environment you live in.
Tiny Home Tips for a Temperate (Mild) Climate
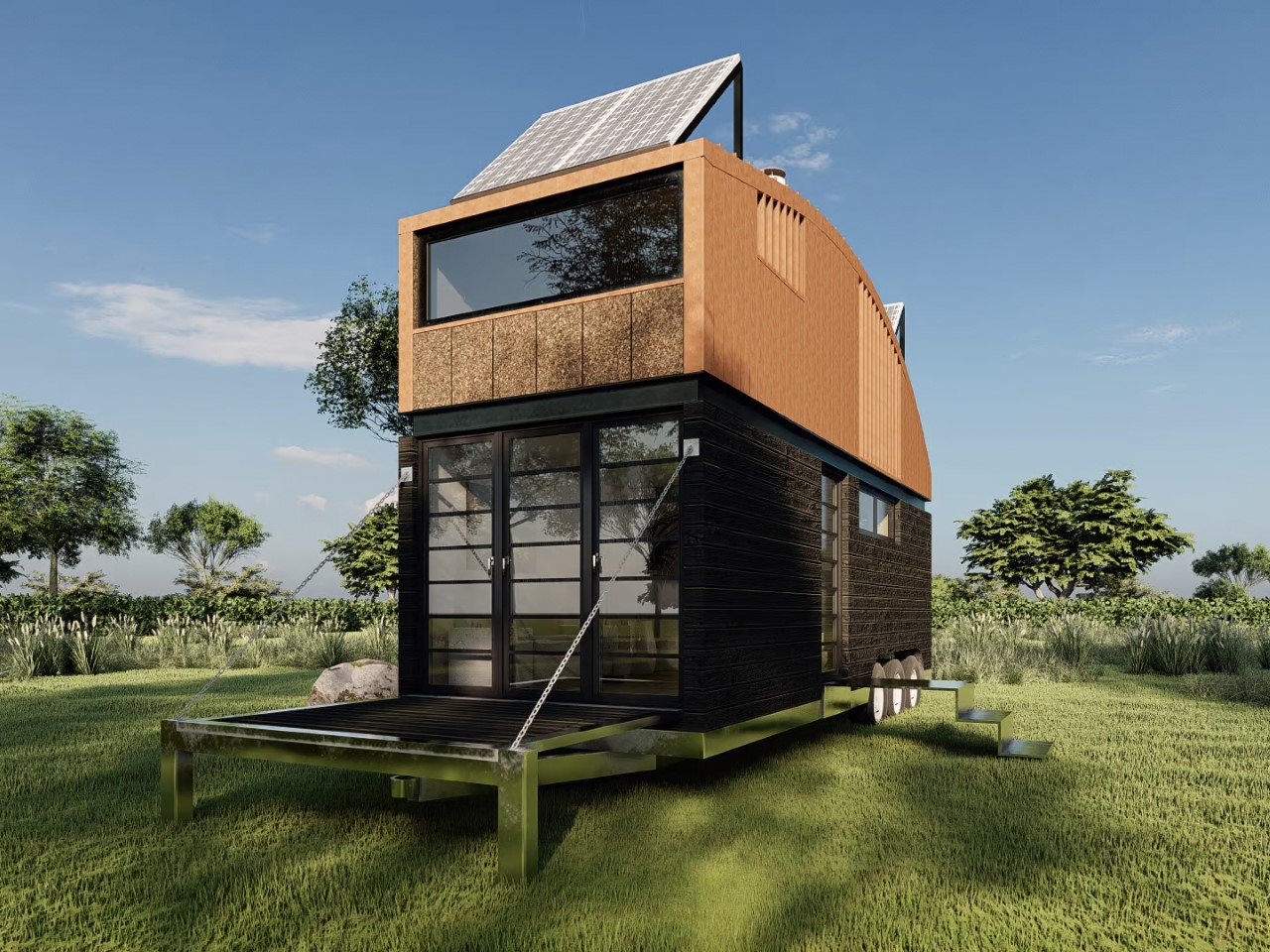

1. Effective Insulation: Keep it Cozy Year-Round
One of the best decisions you can make for a tiny home in a temperate climate is to invest in effective insulation. Think materials such as thermal insulation that can maintain comfortable indoor temperatures regardless of the season. Double-glazed windows are a game-changer. They help keep the heat out during summer and retain warmth in winter, making your tiny home’s energy consumption significantly lower.
2. Natural Light: Brighten Your Space Naturally
Maximizing natural light is another key consideration. Large windows and skylights can transform a small space into a bright, airy sanctuary. Light-colored interior finishes, such as white walls or pale wood flooring, help reflect sunlight, enhancing the overall sense of space. This is not just about aesthetics; natural light positively impacts mental health and reduces the need for artificial lighting, saving energy.
3. Seasonal Adaptability: Adjust Your Spaces with Ease
A temperate climate sees changes in temperature and humidity throughout the year. Designing flexible spaces or modular elements within your home can allow you to adjust your living conditions easily. Heating and cooling systems should be tailored for moderate variations, ensuring that your home remains comfortable through the seasons without significant energy expenditure.
4. Ventilation: Fresh Air Circulation
Proper ventilation is crucial for maintaining air quality in your tiny home. Design your windows and vents to promote cross-ventilation, ensuring fresh air circulates freely. Ceiling fans or mechanical ventilation systems can supplement natural airflow, especially on those days when opening windows isn’t an option.
5. Sustainable Materials: Eco-Friendly Living
Choosing locally sourced, sustainable building materials not only reduces your carbon footprint but also supports local businesses. Consider green roofs or walls, which can offer additional insulation and improve air quality, making your tiny home more eco-friendly and enjoyable to live in.
Tiny Home Tips for a Tropical (Humid) Climate
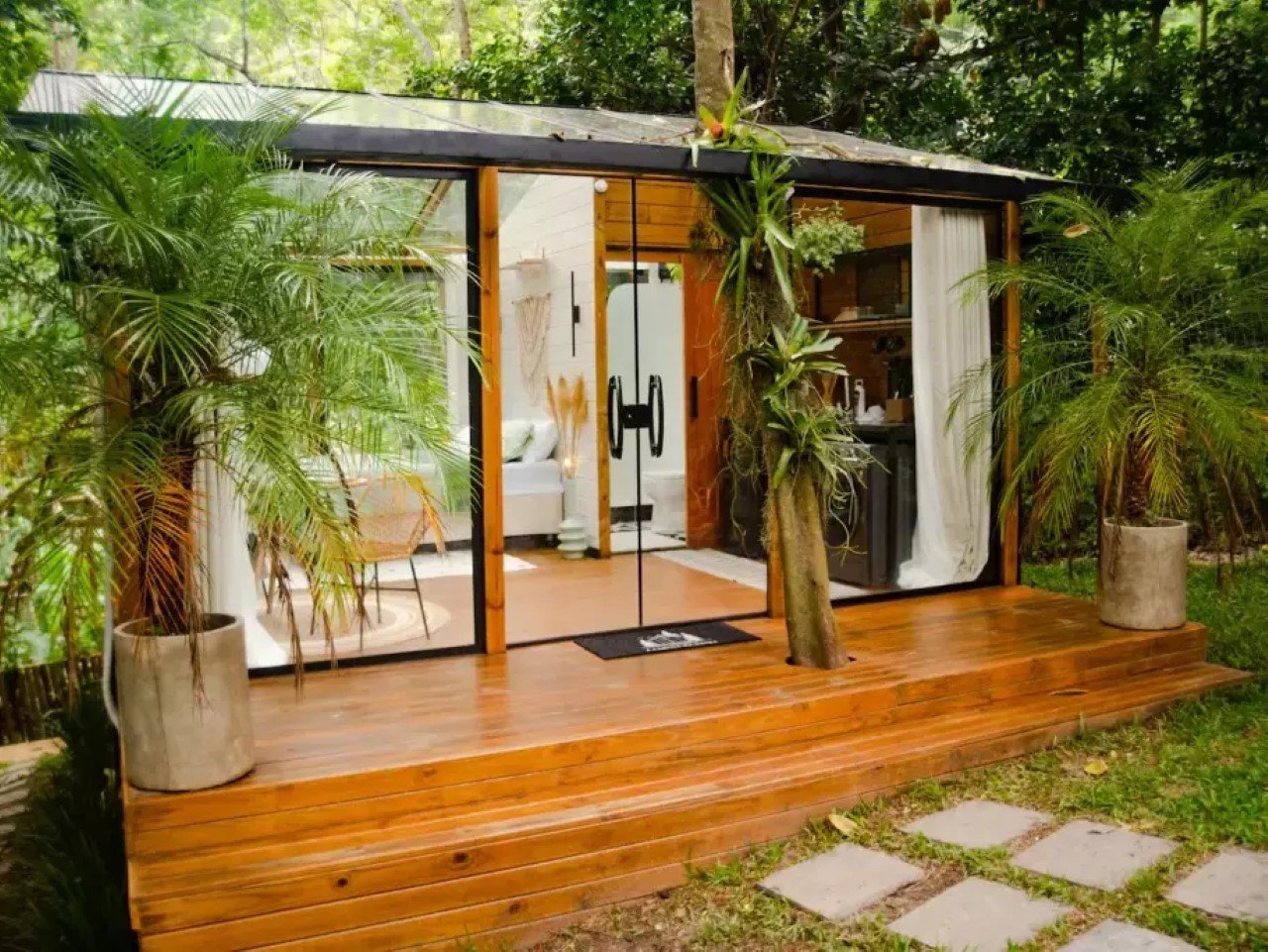

1. Moisture-Resistant Materials: Combat the Dampness
In tropical climates, dealing with high humidity and frequent rainfall is essential. Bamboo wood is a superb choice, as it is naturally resistant to moisture. Metals that don’t rust and mold-resistant paints and finishes will also extend the life of your home, reducing maintenance costs and efforts.
2. Ventilation: Natural Breezes to prevent that Musty Feeling
Strategic window placement and the use of louvers can help maximize airflow, keeping your home cool and dry. Elevated flooring is another effective strategy, allowing air to circulate underneath the house and preventing moisture build-up and that dank, musty feeling that you can often get from homes with the windows shut for too long.
3. Shading: Beat the Heat and Rain
To combat the relentless sun, incorporate overhangs and pergolas into your design. These elements protect against direct sunlight and rain, while light-colored and reflective roofing materials can reduce heat absorption, keeping the indoor spaces cooler.
4. Cooling Strategies: Passive Solutions to Stay Comfortable
Incorporate natural cooling techniques such as wide eaves and verandas, which shield your home from the sun while allowing breezes to flow through. Passive cooling systems, like roof ventilation or even small water features, can also play a significant role in keeping your tiny home comfortably cool.
5. Outdoor Living Spaces: Expand Your Living Area
Designing for outdoor living spaces in tropical climates not only expands your living area but also helps mitigate indoor heat. Equip these areas with weather-resistant furniture and fixtures, creating a comfortable and inviting addition to your tiny home.
Tiny Home Tips for an Arid (Desert) Climate
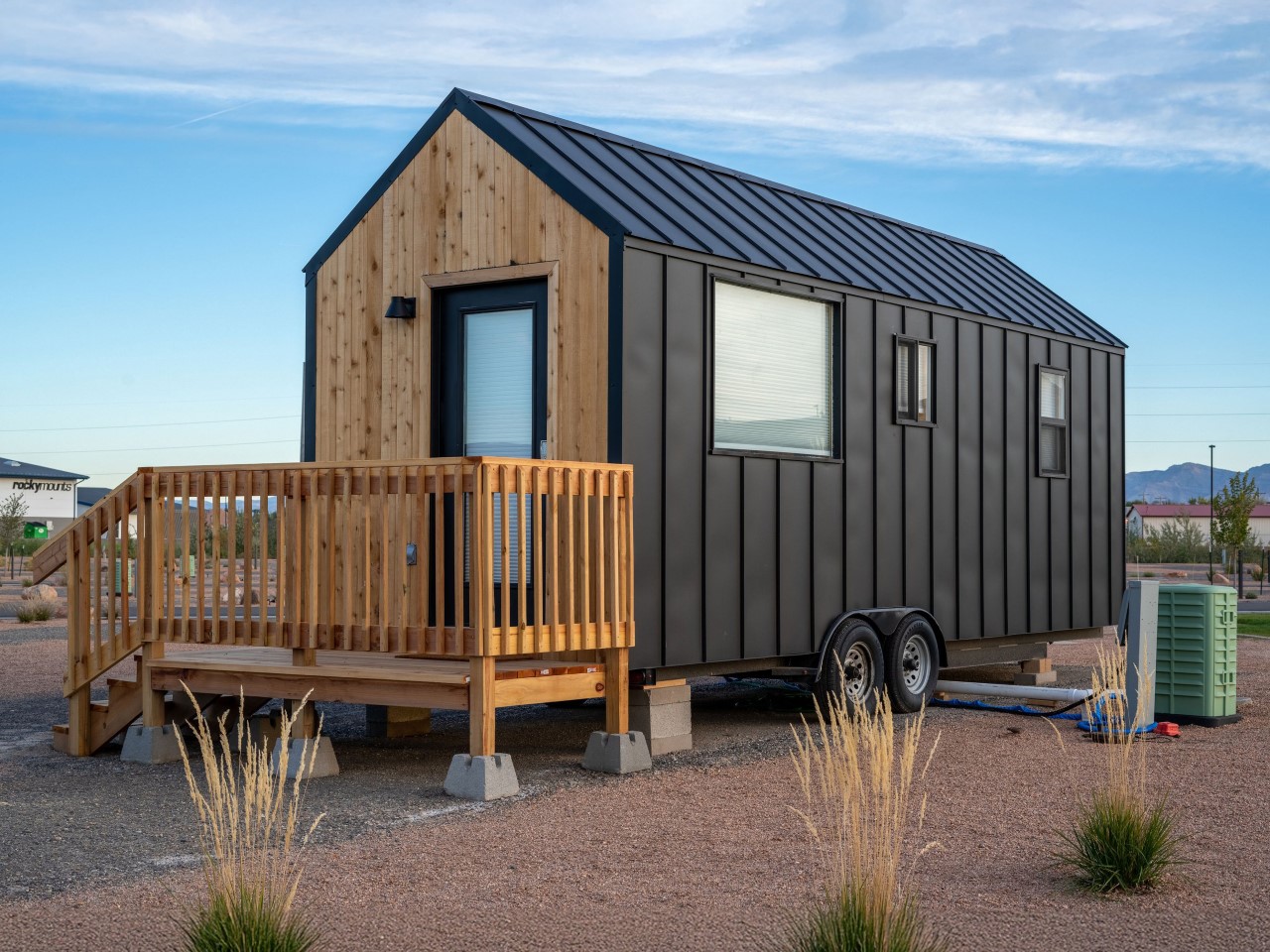

1. Thermal Mass: Regulate Temperature Naturally
In desert climates, the drastic temperature changes between day and night call for materials with high thermal mass, such as adobe or concrete. These materials absorb heat during the day and release it at night, helping to regulate your home’s temperature naturally.
2. Shade and Cooling: Keeping Cool in the Desert Heat
Incorporate shading devices like awnings and pergolas to reduce heat gain. Evaporative cooling systems, which use water to cool the air, can be incredibly effective in these dry climates, providing an energy-efficient means of temperature control.
3. Water Conservation: Make Every Drop Count
Water is a precious resource in arid environments. Implement rainwater harvesting systems to collect and store what little rainfall you get. Low-flow fixtures and greywater recycling systems can help minimize water use, making your home more sustainable.
4. Solar Energy: Harness the Sun’s Power
Solar panels are a must in sun-drenched regions. With strategic placement, these panels can provide a significant portion of your home’s energy needs, reducing reliance on non-renewable sources and lowering bills.
5. Landscape Design: Drought-resistant and Beautiful
Opt for xeriscaping—a landscaping method that uses drought-resistant plants. This reduces the amount of water needed for gardening while still offering aesthetic benefits. Efficient irrigation solutions can further minimize outdoor water use, aligning your tiny home with sustainable living practices.
Tiny Home Tips for a Cold (Snowfall) Climate
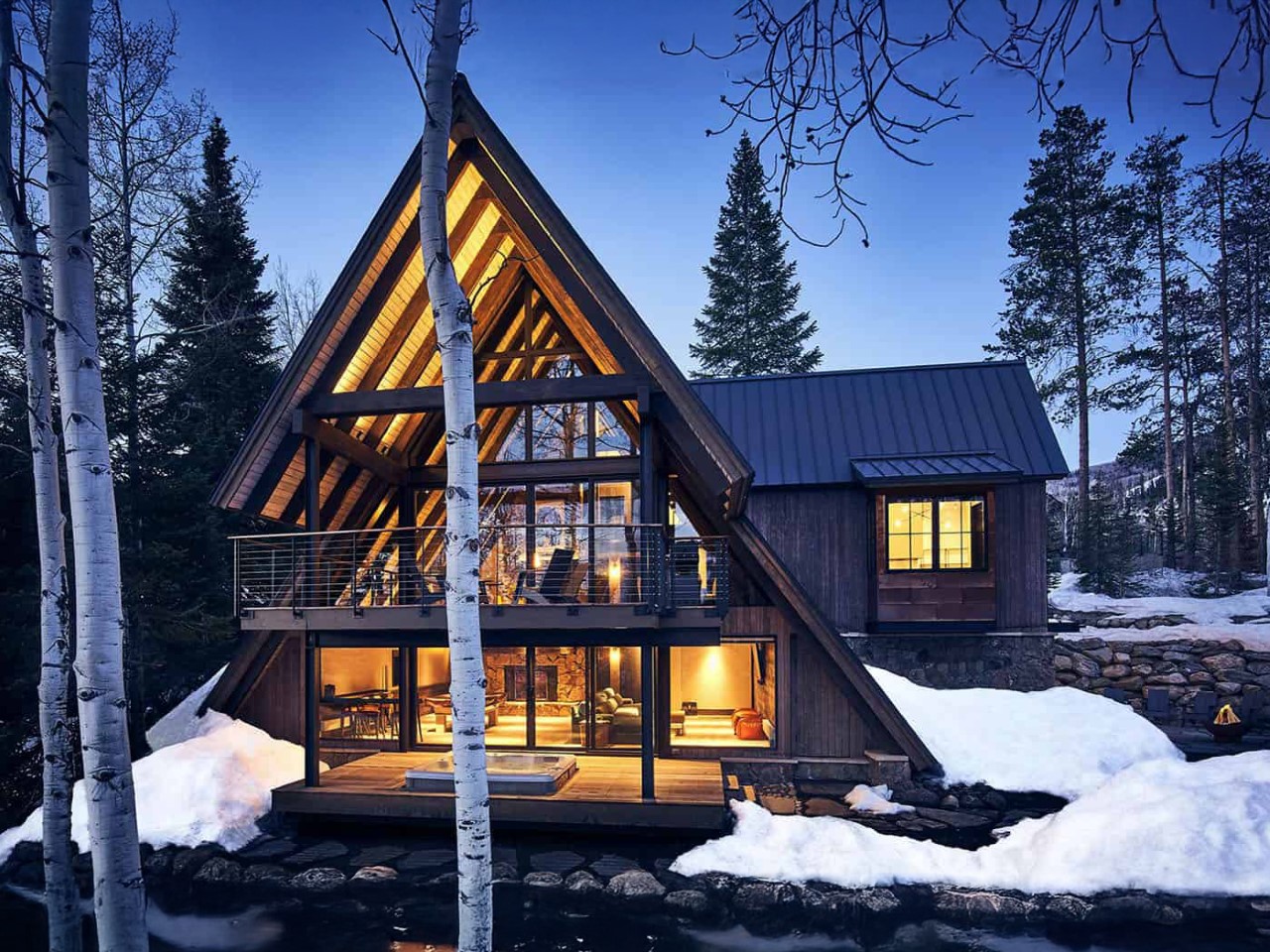

1. Insulation and Heating: Stay Warm All Winter Long
For areas experiencing significant snowfall, proper insulation is paramount. Materials like spray foam or rigid foam board provide excellent thermal resistance. Efficient heating systems such as radiant floor heating or wood stoves can ensure your home remains warm and cozy.
2. Snow Load Consideration: Keep Your Roof Safe
Your roof should be designed to handle heavy snow loads. This typically means a steep pitch and possibly a metal roofing material to facilitate snow shedding, preventing structural damage.
3. Energy Efficiency: Keep the Cold Out and the Warmth In
Triple-glazed windows are an excellent investment in colder climates. They provide superior insulation, keeping the heat inside and cold air out. Pair these with energy-efficient appliances and fixtures to further reduce your energy consumption.
4. Weatherproofing: Shield Against the Elements
Sealing and weatherproofing are vital to prevent drafts and heat loss. Use durable, weather-resistant exterior cladding to protect your home from the elements, ensuring longevity and reduced maintenance.
5. Access and Safety: Ease Your Winter Woes
For those snowy winters, incorporating heated walkways or driveways can prevent ice build-up, making daily access safer. Design considerations should also include adequate storage for winter gear and provisions, ensuring that your tiny home remains functional during the cold months.
Tiny Home Tips for a Coastal Climate
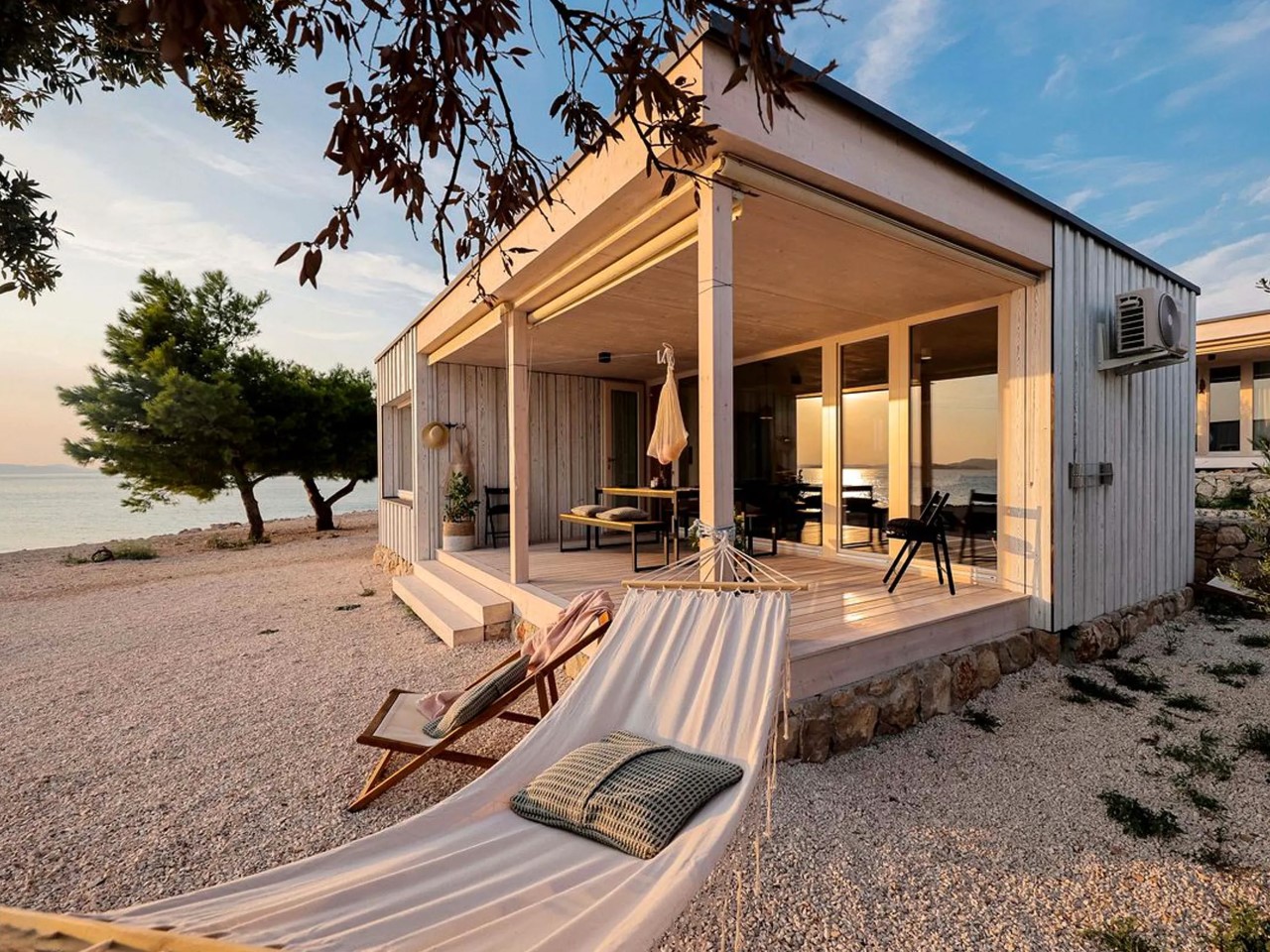

1. Salt-Resistant Materials: Protect Against Corrosion
Living near the sea presents unique challenges, primarily due to salt. Choose materials like composites or treated wood that can withstand salt corrosion. Non-corrosive metals, such as stainless steel or aluminum, are also excellent options for fixtures and structural elements.
2. Elevated Design: Guard Against Flooding
An elevated structure helps prevent flooding and water damage, which are common issues in coastal areas. Sturdy foundations are necessary to withstand coastal storms and wave impact, ensuring the safety and durability of your tiny home.
3. Wind Resistance: Build to Withstand Strong Winds
To combat high winds, incorporate aerodynamic designs that reduce resistance. Reinforced structural elements, such as hurricane ties or braced frames, are critical in providing additional stability and safety.
4. Humidity Control: Maintain a Healthy Environment
Dehumidifiers or humidity control systems are essential in coastal climates. Proper ventilation is key to preventing mold and mildew growth, ensuring that your living space remains healthy and comfortable.
5. Views and Natural Light: Embrace the Scenic Beauty
One of the joys of coastal living is the view. Large windows and open layouts can maximize these ocean vistas, making your tiny home a serene retreat. Outdoor living spaces that blend seamlessly with the natural environment not only enhance the aesthetic appeal but also expand your living area.
Designing a tiny home that harmonizes with its environment is an exercise in both creativity and practicality. The benefits are manifold: from increased comfort and efficiency to sustainability and aesthetic appeal. It requires a nuanced understanding of local climate challenges and opportunities. By using the right materials and design principles, you can create a tiny home that not only stands the test of time but also provides a sanctuary in harmony with nature.
Remember, your tiny home is more than just a place to live— it’s a reflection of your lifestyle and values. Whether you’re basking in the sun’s tropical warmth, savoring the tranquility of the coast, or enjoying the crisp air of a snowy landscape, your tiny home can be your personal oasis, thoughtfully designed for comfort and sustainability. So, as you embark on this journey, consider these tailored recommendations to make every square foot of your tiny home a testament to smart, climate-conscious design.
The post Top Tips For Designing Your Tiny Home Based on Climate and Environment first appeared on Yanko Design.























 Technology for ultra-precise tracking, so you can leave the steering to the X1 PRO or PROMAX and focus on getting the shot.
Technology for ultra-precise tracking, so you can leave the steering to the X1 PRO or PROMAX and focus on getting the shot.